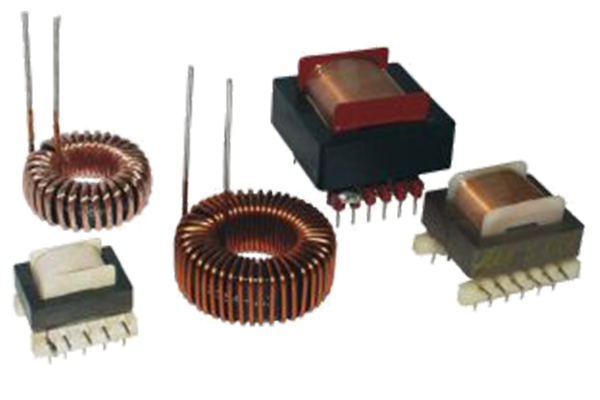
Pulse transformers are indispensable
components in high-frequency power conversion systems. Their ability to transfer electrical
pulses with precision while maintaining galvanic isolation makes them essential for various
applications, from control circuits to power stages. With a range of standard and custom design
options, pulse transformers offer unparalleled flexibility and performance. By understanding the
key features and benefits of pulse transformers, engineers and designers can make informed
decisions, ensuring the optimal performance of their high-frequency power converters.
Invest in pulse transformers to enhance the
safety, efficiency, and reliability of your power conversion systems. Whether you require a
standard transformer or a custom-designed solution, pulse transformers are the key to achieving
superior performance in your high-frequency applications. Contact us today to place an enquiry
and discover how our pulse transformers can meet your specific needs.